Heat Staking Fundamentals
Introduction to Heat Staking
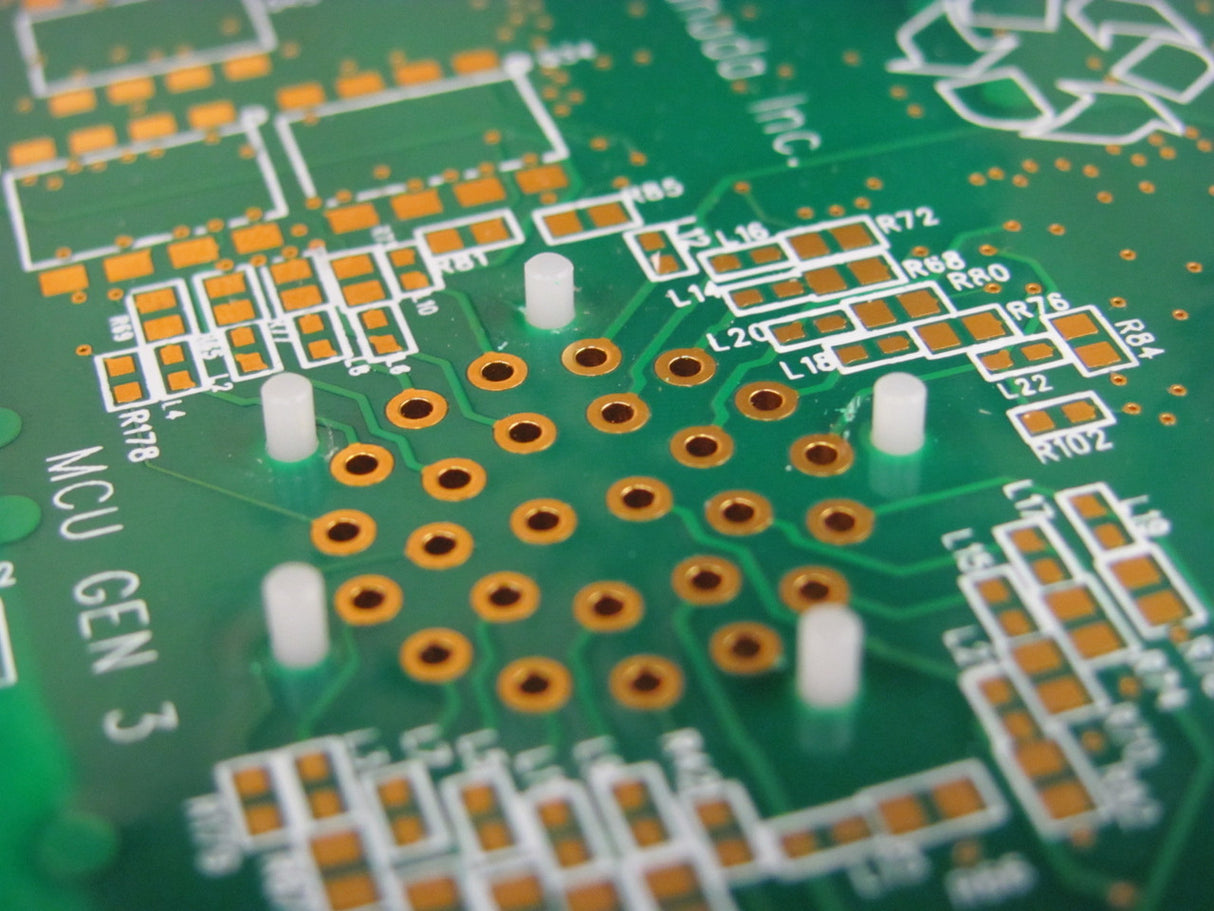
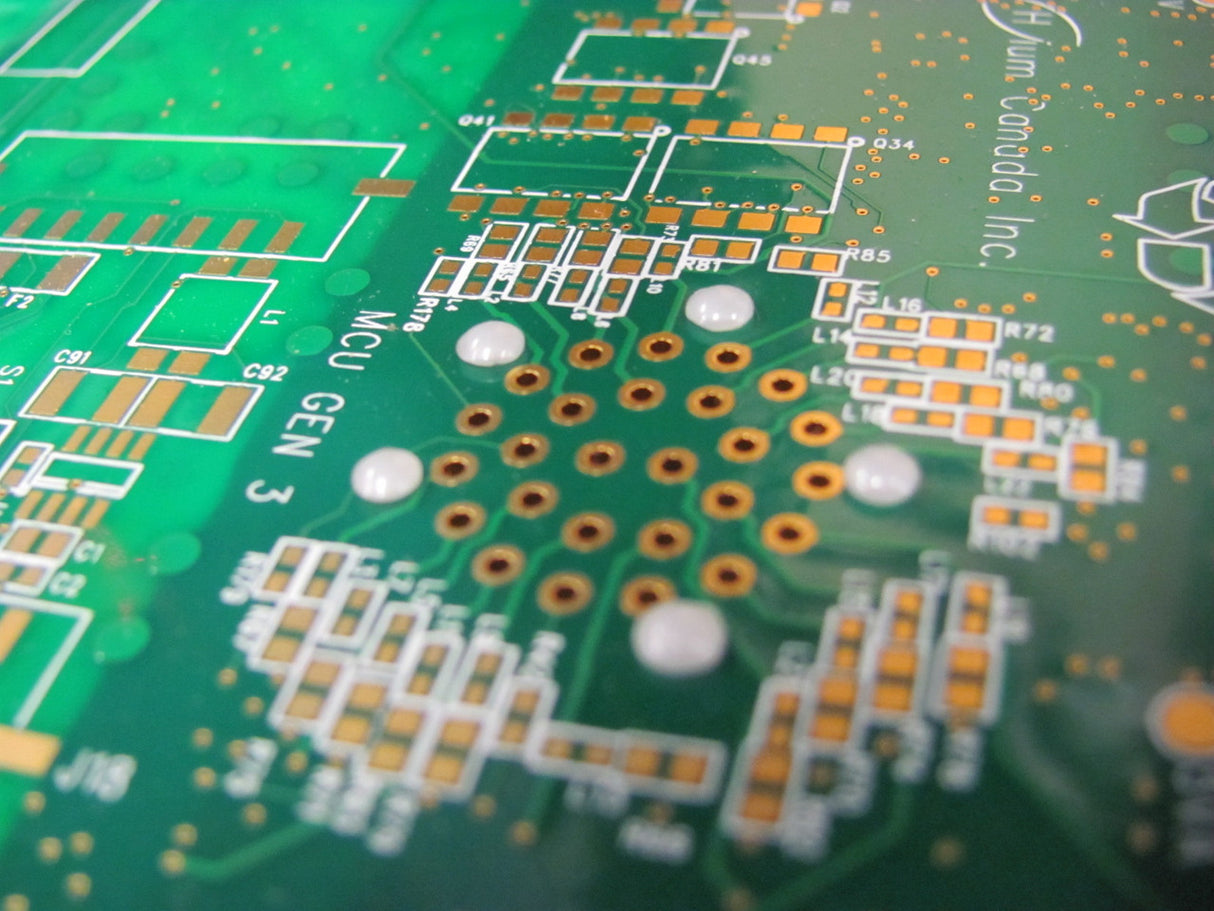
Sonitek's Heat staking process is a thermal joining & cooling process that utilizes precisely controlled heat and applied force to join or seal any material to thermoplastic materials. Typical examples of materials to be joined include PCB's, Busbars, Electrical Contacts, Sheet Metal, and many other metal components as well as installing threaded inserts and torque limiters into thermoplastic housings.
Heatstaking is widely used globally in thousands of applications where traditional fastening methods such as adhesives, screws, or rivets are unsuitable and especially where the ultrasonic process damages components, marks the plastic surface or suffers from horn face wear quickly resulting in loose stakes and costly tool replacement.
Sonitek's Heatstaking process provides a durable and very repeatable result with minimum tool wear, making it ideal for complex assemblies in various industries including Medical, Automotive, Battery, Aerospace, Appliance, or any other industry using thermoplastics in their products.
Technical Process
The Sonitek heat staking process involves several critical steps to ensure a robust and reliable bond:
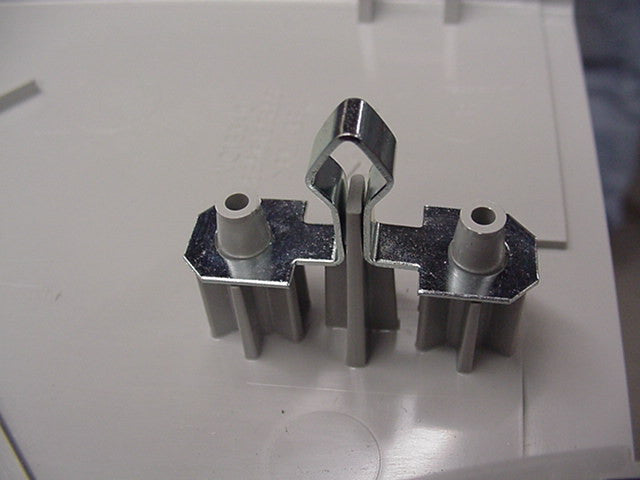
Part Positioning: The plastic part is well supported and perfectly aligned into a fixture located on the Sonitek machine base with the plastic bosses (solid or hollow) and the substrate assembled and ready for processing.
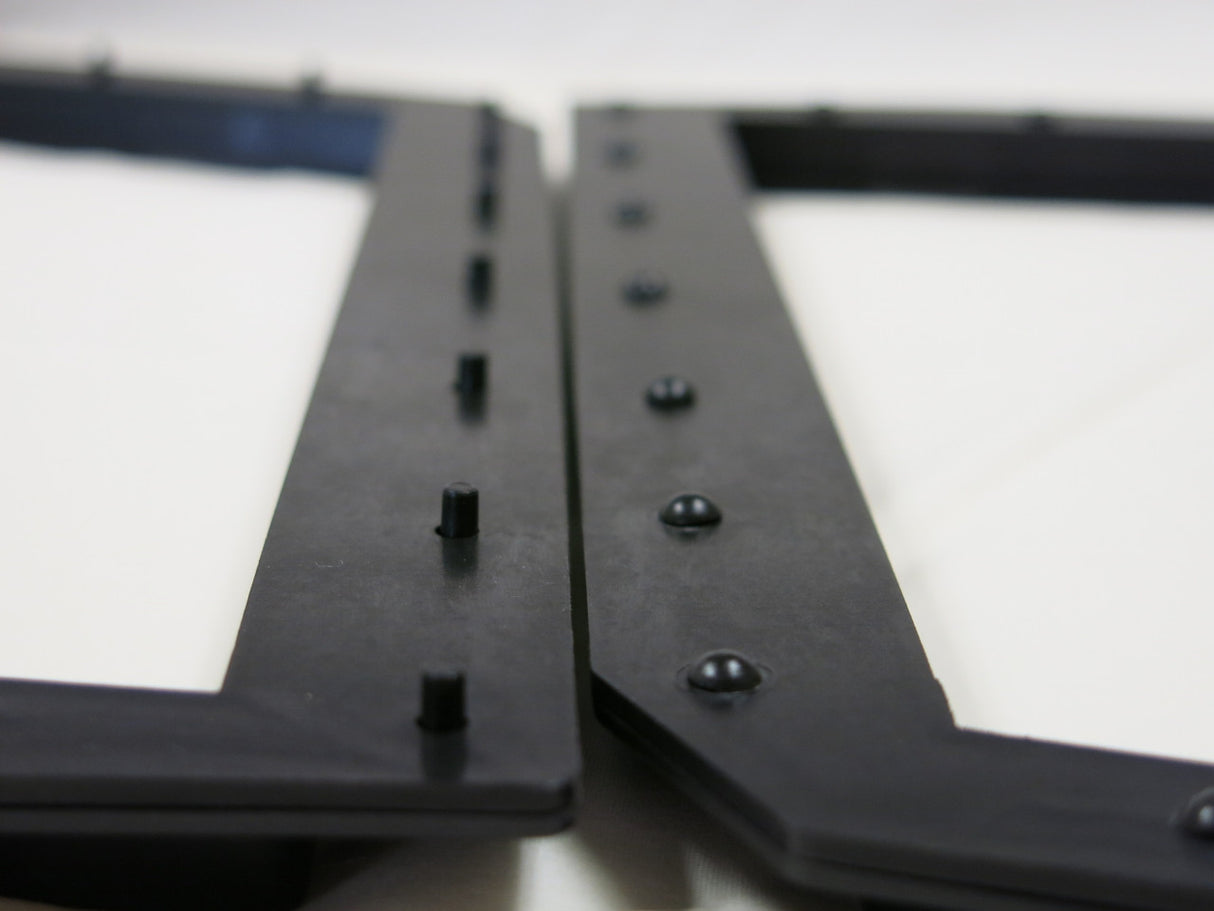
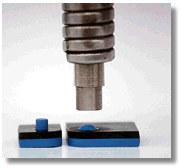
Heating: The tooling (platen or probe) equipped with custom made "staking tips" with a designed domed cavity or other shape descends onto the part. Precise Heat, Force and Speed is applied, heating the plastic to just above its glass transition temperature (Tg), where it becomes malleable.
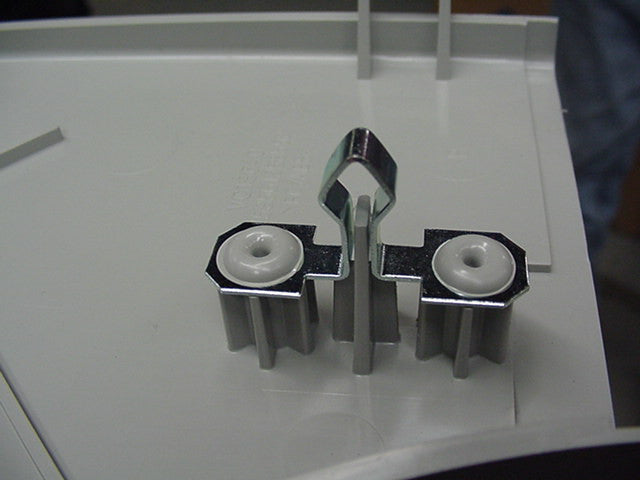
Forming: Simultaneously, force is applied, causing the heated plastic to remold and flow shaping into the cavity of the tool, forming the required shape and attaching to the adjacent part.
Cooling: While maintaining force, the tooling is usually cooled using Sonitek cooling methods. This solidifies the plastic, ensuring a strong, fixed joint with high aesthetic results.
Release: The cooled tooling is retracted, and the finished assembly is removed from the fixture.
Advantages of Heat Staking
- Material Compatibility: Can join a wide range of thermoplastics, including polycarbonate (PC), glass-reinforced nylon (GFN), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS).
- Design Flexibility: Allows the use of the base material to form the stud without design changes or additional materials or fasteners helping to reduce weight, waste and cost.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Eliminates the need for consumables such as adhesives or screws or other expensive processes like ultrasonic or laser machines.
- Precision and Repeatability: Provides consistent results with precise control over temperature, force, and cooling.
- Low Stress: Minimizes stress on the assembly, preserving the integrity of delicate components.
- Extremely low maintenance costs.
Heat Stake Design Variations
Various heat stake designs are available to suit different applications, each offering unique benefits:
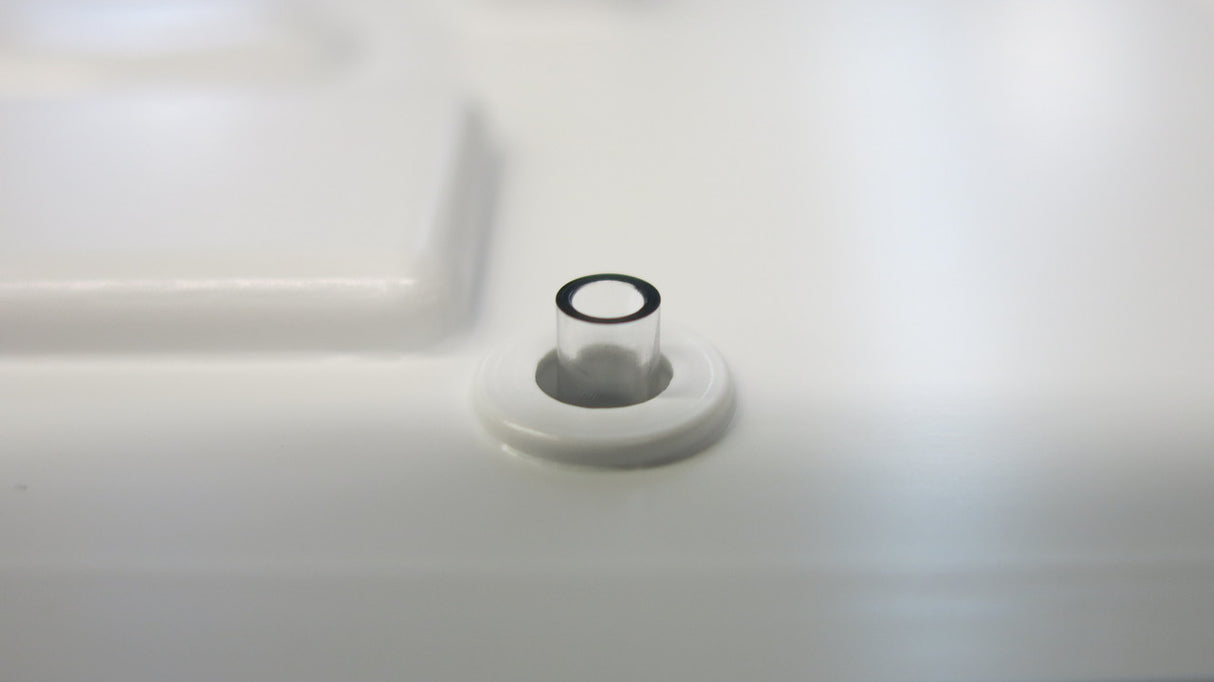
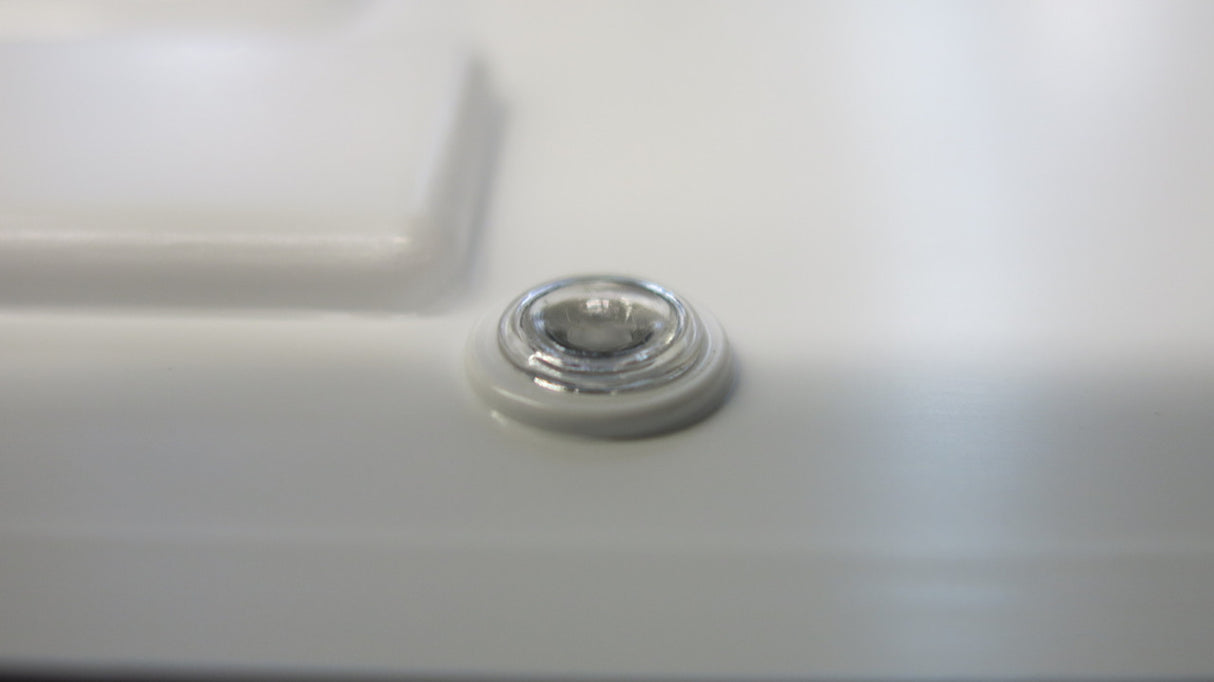
- Dome Shape: Ideal for small-sized pins.
- Double Dome Shape: Used for medium-sized pins.
- Tubular or Hollow Stake: Suitable for large-sized pins, providing strong retention with minimal material.
- Rollover or Captive Stake: Ensures secure fastening, particularly in dynamic applications.
Comparative Advantages of Heat Staking Technology
| Feature | Heat Staking | Cold Staking | Ultrasonic Staking |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low heat affected zone protects adjacent electronics | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Very fast operation | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Can deform glass-filled plastic without embrittlement | ✓ | ||
| Can stake materials with up to 60% glass fill | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Low stress on the stud | ✓ |
Typical Applications
Heat staking is employed in various industries, including automotive, medical, aerospace, battery and consumer electronics.
The process is suitable for:
- Thermoplastics (amorphous or semi-crystalline)
- Metal to plastic joining
- PCBs, Gaskets, leak tight seals, membrane and filter seals
- High temperature materials including: (PEEK) (PA) (PI) (PAI) (PPS) (PEI) (PES) (PPSU) (PEKK)
- Glass filled materials and Flame Retardants
- Even Polyethylene (PE) and PTFE and PFA!
- Complexed geometries with multiple levels and locations
Contact Us
For more detailed information and technical specifications on our heat staking solutions, please contact us.